OHDSI Databricks User Group Developer How-tos
Git and Github Quickstart Guide
This is the quick start guid for Git and Git hub.
Git is a version control system that is used by virtually all open
source (and other large) projects.
This quick start guide shows how to download and install a Git client,
how to create a Github account, and how to get permissions for an
existing Github project (like this one!).
Summary
The following steps are detail below.- Install a Git Client
- Create a Github Account
- Fork a Project
- Clone the Project
- Make Your Updates
- Commit Your Updates
- Create a Pull Request
Install a Git Client
Instructions for installing a Git client are
here .
Create a Github Account
Go to https://github.com/ and select “Sign Up”.Follow the instructions there to create your Github account.
Once you’ve created your account you can check your user name by
selecting the icon in the upper right corner and then selecting “Your
Profile” (select the link at the bottom of the screen to skip the
tutorial first).
Your user name should be on the left side of the screen.
Fork the Project
Login to Github with the account you would like to use for this work.
Navigate to the project you want to edit, in this case https://github.com/OHDSI/DatabaseOnSpark.
Select the “Fork” drop down and then select “Create a new fork” as shown
below.
Clone the Repository
“Cloning” the repository just means pulling a copy of the files down to
your local machine in a way that any changes you make can be merged back
into the repository.
Open a cmd prompt and navigate to the directory where you would like the
project to live.
After you’ve install the client you will need to issue the following two
commands (this is usually a one time thing).
git config –global user.email “the-email-you-registered-withc@yourhost.com”
git
config –global user.name “YOUR_USERNAME”
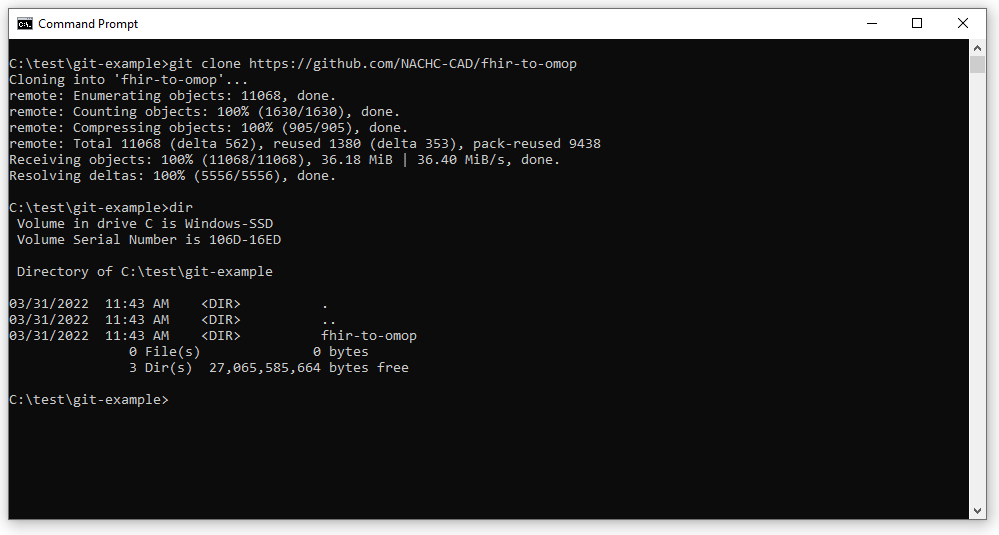
To clone the repository, enter the command:
git clone
<paste-repository-name-here>
Make Your Updates and Commit
Change to the directory that was downloaded from the clone
process.
Make your updates to the files.
When you are done with your updates, commit the changes using the
following Git commands.
git add -A
git commit -m “a
very useful and meaningful message”
git push origin
Configuring Client Security
The first time you try to push your updates you will be asked for a username and a password. Your username/password will not work as github has moved to only allowing token based authentication for this activity. To get a token follow the Create Token instructions. Then use your username for the username and the token for the password. Note that pasting the token in as the password can be a little tricky as the cmd prompt does not change when you do the paste. I find the best way to do this is to click the top border of the cmd window to set the focus to that window. Then, right click in the window (this does the paste). Then, press enter.
Changing Client User
After the first time you authenticate to the server the git client
saves your credentials. This way you do not have to re-authenticate
every time you would like to push new changes to the server. To change
the user that git uses to authenticate is a little tricky. You need to
open “Credential Manager” (search under windows).
Then select the Windows option.
Then scroll to the git:https://github.com entry and select remove.
The next time you try to push code to the server you will be
asked to enter your username/password (which is really
username/token).
Create a Pull Request
A pull request is the mechanism that is used to let the owner of a repository know you have committed changes to your fork that you would like pulled into the main repository for the project. To create a pull request, navigate to your copy (fork) of the repository (see below). Select the link that indicates you have made changes to this code base (in this case, the link that reads “3 commits ahead”)If everything looks good, press the create pull request button.
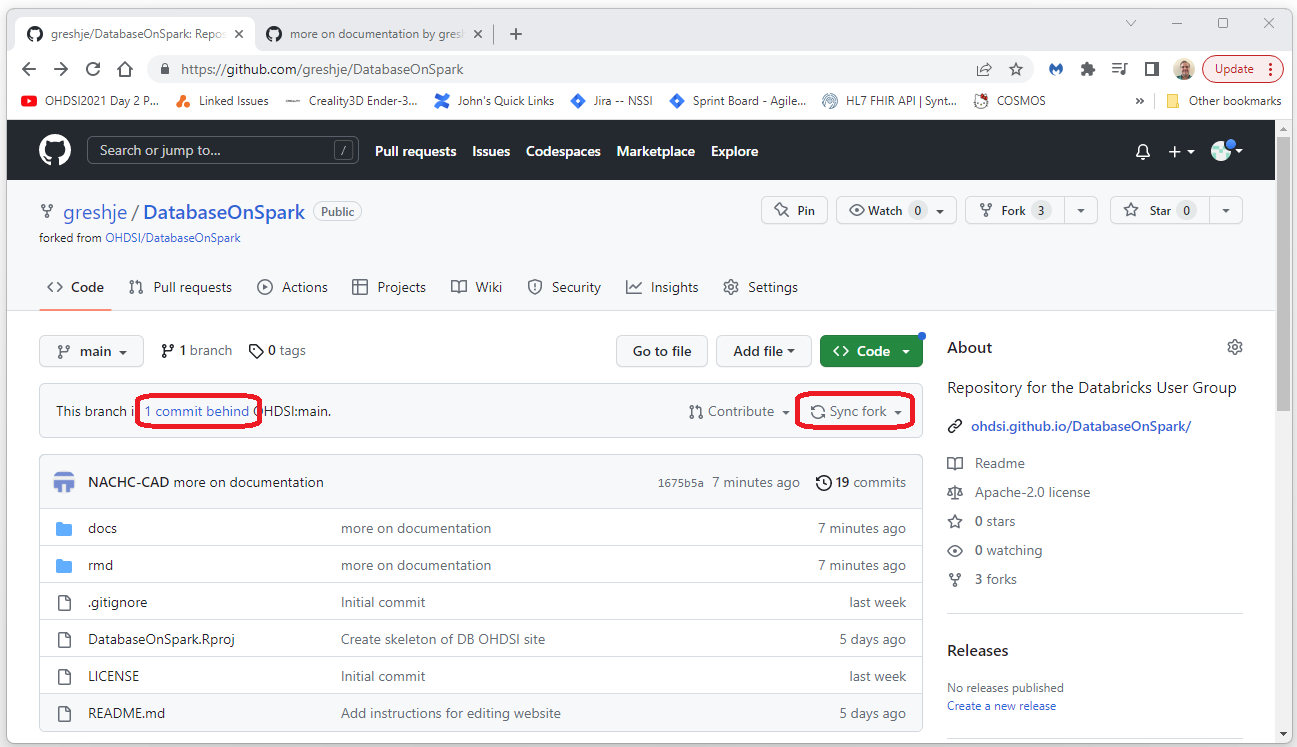
Update Your Fork
After your (or any) pull request has been accepted your fork will
have a link indicating that you are behind the original (source)
repository. (e.g. the link “1 commit behind” in the screen shot below).
To get your repository upto date, do NOT click on the link. Click on the
“Sync Fork” button shown in the screen shot below.
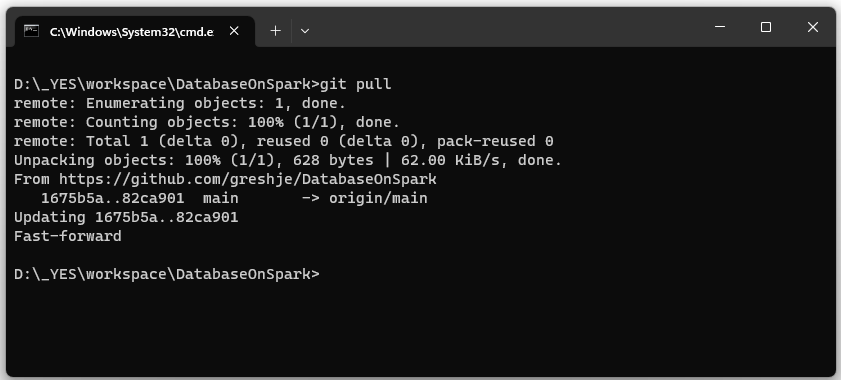
The run “git pull” on your local host.
 OHDSI Databricks User Group
OHDSI Databricks User Group